-
Sale!
Radtrak³®: home radon testing kits
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Rapidos®: short-term home radon testing kits
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
Radtrak³®: radon testing kits for workplaces and schools
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -
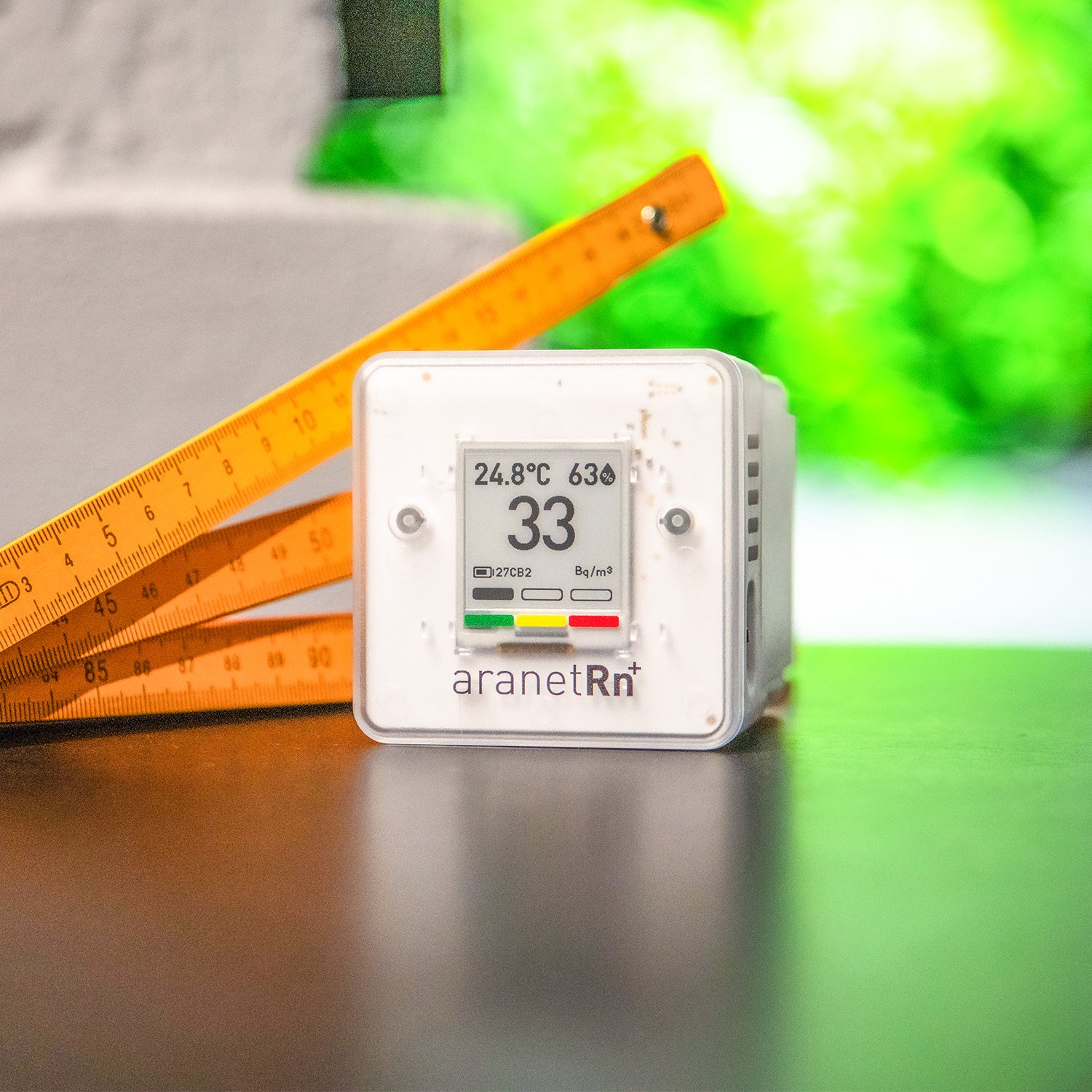
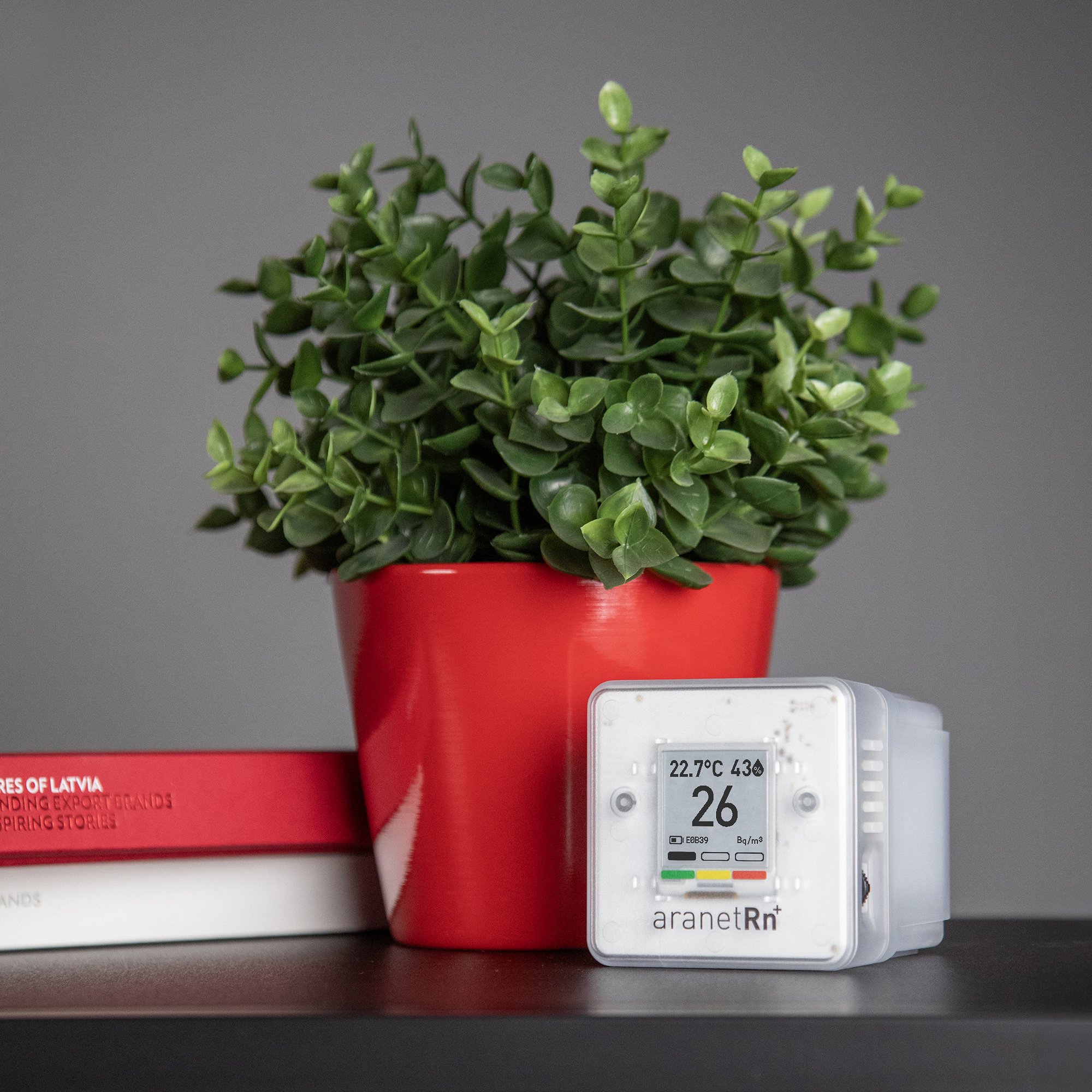
Aranet Radon Plus: digital radon monitor for homes
Add to basket -
SPIRIT® Radonlogger: digital radon monitor for homes, schools, and workplaces
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
30+ years of
experience
Customers in over 80
countries
20,000,000+
detectors sold worldwide
15,000,000+
measurements performed
UK radon gas testing and measurement, from the world’s leading laboratory
With over 30 years’ radon gas testing experience, at Radonova we pride ourselves on our industry-leading instruments and procedures. International comparison tests prove our measurement standards to be of the highest accuracy and quality, while our innovative technologies and fast, cost-effective service have led us to produce and analyse over six million radon detectors to date worldwide.
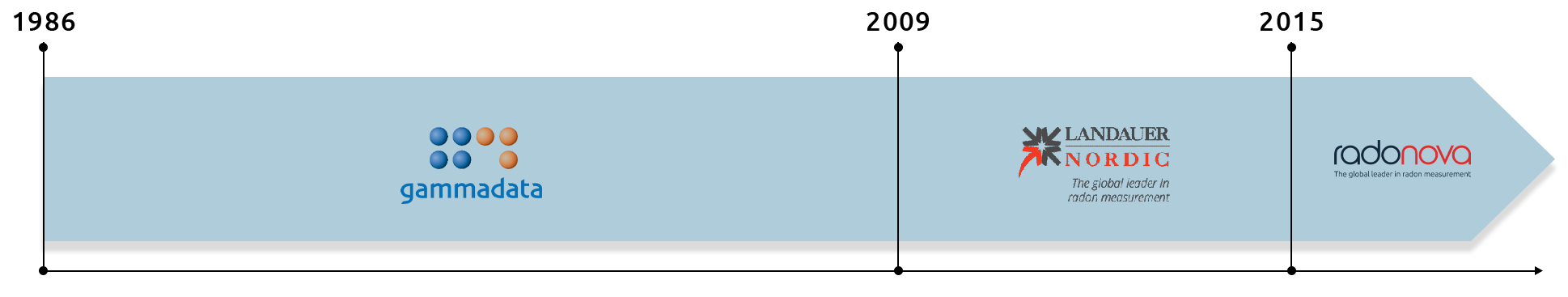
Our history
Radonova Laboratories, formerly Landauer Nordic and Gammadata Mättekinik, was founded in 1986 following the Chernobyl nuclear accident. After the disaster, the Swedish government commissioned a group of researchers from Uppsala University to measure the fallout, and a young company with a bright future was born.
Radonova is now a global leader, conducting large-scale radon measurement in over 80 countries. We have built a strong reputation for our instrument quality, professional values, and innovative technologies.
Radonova Laboratories is part of the Lagercrantz group.
Frequently-asked questions about radon gas
Why choose Radonova?
Radonova is the UK’s only ISO17025-accredited radon testing laboratory, and our long-term radon testing kits are fully validated by the UK Health Security Agency.
We have over 30 years’ experience, with international comparison tests proving our testing and measurement standards to be of the highest precision and quality.
Why is radon gas dangerous?
Radon gas is the second most common cause of lung cancer in the UK after smoking. According to UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) around 1,100 lung cancer deaths are attributed to radon gas exposure each year. Radon gas is radioactive – when inhaled, it emits alpha radiation, harming tissues which can lead to lung cancer over time.
Where does radon gas come from?
Radon gas is a decay product of Uranium238, found naturally in soil, which seeps into buildings through tiny cracks in their walls and foundations.
Homes, workplaces and schools are heated, insulated indoor environments, in which high concentrations of radon gas can quickly build up.
How do I measure radon gas levels indoors?
Radon gas levels can be measured easily, accurately and affordably using a validated testing kit. Due to weather conditions, temperatures, and atmospheric pressure, radon gas levels fluctuate, so UKHSA recommends a testing period of 3-12 months to achieve the most accurate measurement.
Digital monitors are often used for conducting follow-up testing post-remedial work.
How do radon testing kits work?
Our passive Rapidos® and Radtrak³® detectors use a method known as alpha track. Anti-static pods containing film element are placed in different rooms of a building for a set period of time. Combined with normal air, radon diffuses into the pod where it decomposes, releasing high energy alpha particles. This energy creates microscopic tracks on the film, which are then counted using a state-of-the-art image scanner in our laboratory.
Our professional radon instruments are all electronic and use either a mains power supply or LiPo battery.
Is using a radon testing kit complicated?
No, it’s really quite simple! You’ll receive detailed instructions in accordance with UKHSA guidelines along with your testing kit order, but in short, instructions for using our Radtrak³® and Rapidos® detectors are as follows:
- Place your order and receive detectors (quantity dependent on property size) within 2-3 working days
- Place detectors as indicated in your property for the designated timescale (90-365 days for Radtrak³®; 10-90 days for Rapidos®)
- Return detectors to us at the address below for laboratory analysis
- Upon receipt, you can expect to receive your report online within 1-2 weeks
Our professional radon instruments (SPIRIT®, ATMOS®, MARKUS® and ROBIN®) have specific, detailed instructions included.
How do I reduce high radon gas levels?
The World Health Organization (WHO)‘s indoor radon gas target level is 100 Bq/m3. The UK government advises that remedial action should be carried out in residential properties with an average radon measurement of 200 Bq/m3 or more.
School and workplace radon testing has different requirements; read more about these here.
Simple methods exist to reduce high levels of indoor radon gas. Reputable organisations providing mitigation services can be found at UK Radon Association or The Radon Council.
How is radon gas measured and what levels are considered too high?
In the UK, radon is measured in bequerels per cubic metre of air, or Bq/m3.
In UK workplaces, remedial action is a legal obligation in cases where radon levels exceed 300 Bq/m3.
In UK homes, remedial action is advised in cases where radon levels exceed 200 Bq/m3.
The WHO‘s indoor radon target level is 100 Bq/m3.
My report indicates high radon gas levels - what should I do?
Don’t panic! There are methods available to remedy high indoor radon level concentrations – find further details here.
We advise visiting the UK Radon Council and the UK Radon Association, where you’ll be able to find details of specialist mitigation services.
Following mitigation, it’s essential to carry out follow-up testing. Contact us to learn what options are available to suit your requirements.
Digital radon monitors are widely available - can't I just use one of them?
Digital domestic radon monitors might be affordable and look stylish, but they won’t have gone through any certification processes or third-party accreditation. They will also not have been calibrated in any way, rendering measurement data unreliable and likely inaccurate, and for this reason they are not endorsed or validated by the UKHSA.
[activecampaign form=3 css=1]