Radon is a radioactive gas that is colourless and odourless. It comes naturally from the soil because it is formed from the radium present in the rocks of the subsoil. Radium and radon are both included in the radioactive decay chain of uranium.
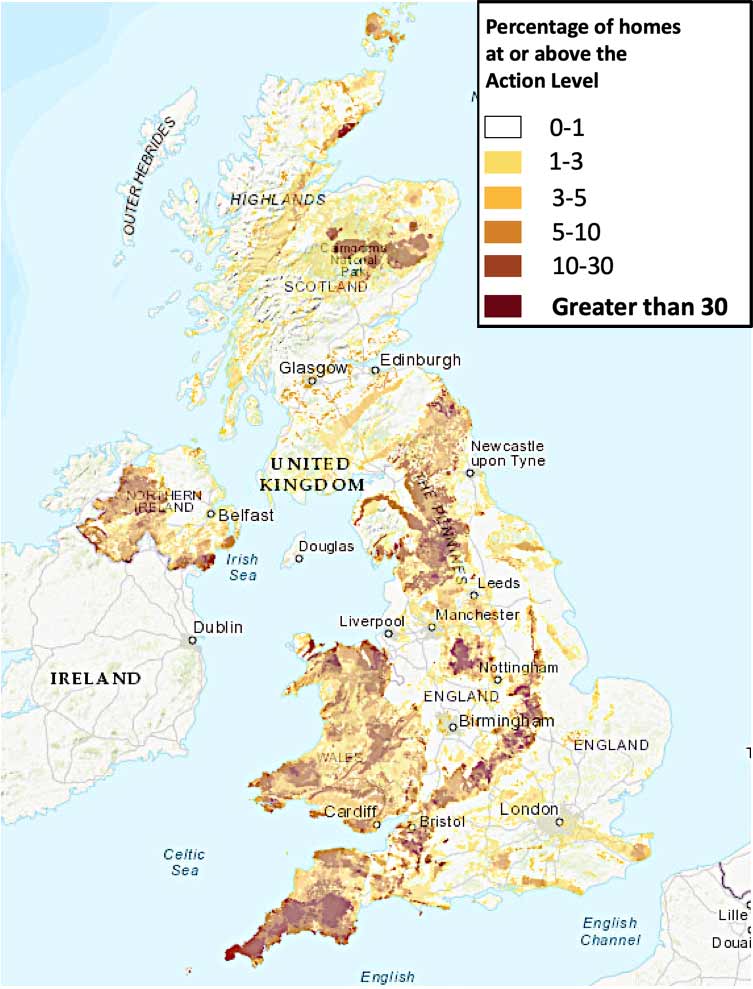
Radon in indoor air is a major public health issue in many countries, including the UK. However, it is often erroneously referred to as a “Cornwall-only” issue, and not high on the agenda of the UK media. Therefore people are often unaware of the health risks that prolonged exposure to radon can lead to, and although regulations exist to test for radon in schools and workplaces, measuring radon in homes is not mandatory.
Why radon is dangerous
Radon is dangerous for three main reasons:
- It cannot be detected by human senses
- Its levels become concentrated in indoor air, where we spend most of our time
- It is radioactive, emitting ionizing radiation as it decays, damaging body cells when inhaled
The World Health Organization (WHO) states that it is proven that radon can cause cancer.
The UK’s National Cancer Institute estimates that radon is responsible for 10% of lung cancer cases diagnosed, and around 1100 deaths from the disease, each year.
Where to find radon
Radon is everywhere.
Although maps exist which indicate areas at risk of radon concentration, it can pose a threat in any indoor area. Radon concentrations in indoor air depend not only on the nature of the soil, but also on the characteristics of buildings.
The most effective way to protect yourself against the risks associated with radon gas is to measure for it.
How to measure for radon
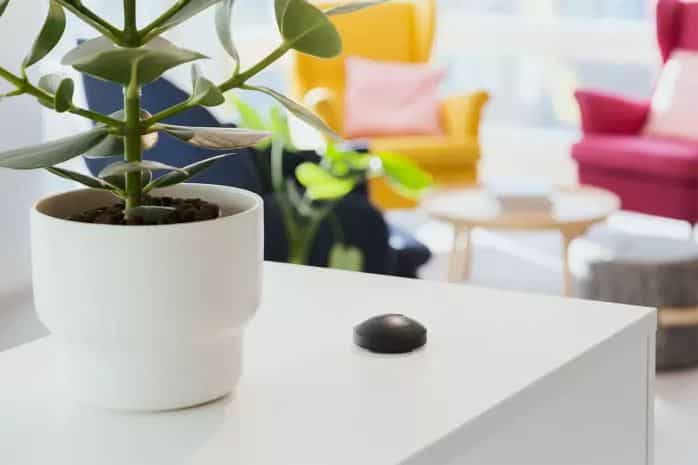
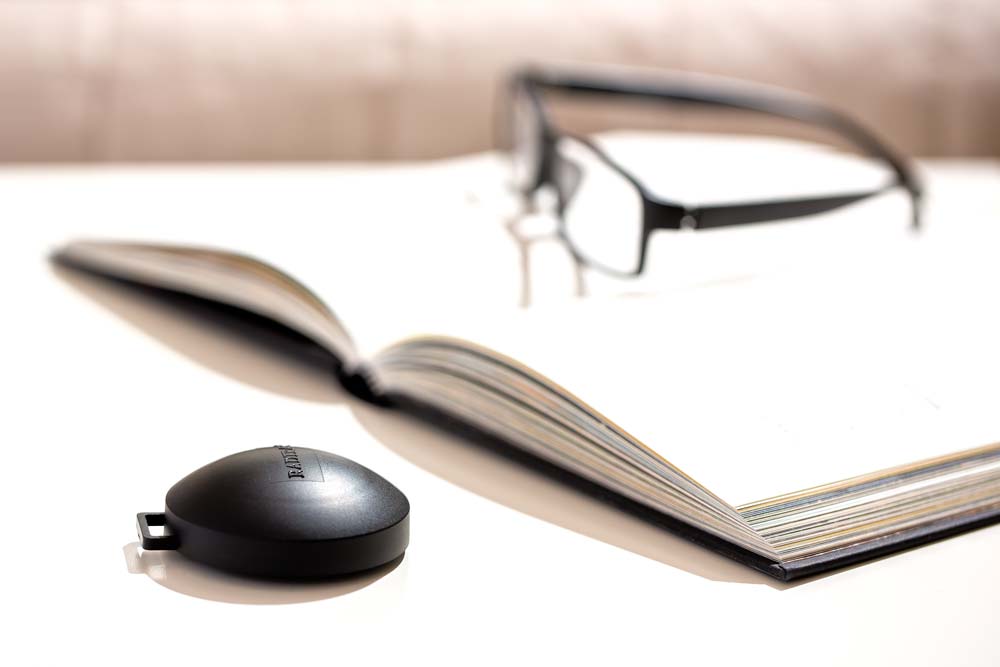
Simply order a test kit from our online store. Our kits are fully validated by the UK Health Security Agency, and we are the only laboratory accredited to ISO-17025 standard in the UK.
Once received, place the detectors as indicated, and return them by post for laboratory analysis at the end of the designated time period. You’ll receive the results within two weeks.
When to measure for radon
- Every 10 years, because cracks can appear as buildings age
- After renovation work, because the characteristics of the building may change
- Following remediation work order to verify that levels have been reduced
If a measurement has never been conducted it is important to do so, and repeat regularly.
Radon reference levels
The radon reference level is the concentration threshold above which radon is deemed to pose a potential risk to health. In the UK, the reference levels are:
- 200 Bq/m³ for homes
- 300 Bq/m³ for workplaces, schools, and public premises
The UK Ionising Radiations Regulations 2017 legislation requires employers to take action if radon levels exceed the workplace and school threshold. Your radon measurement report will indicate whether levels above Bq/m³ threshold are present.